By Dominic Marcellino
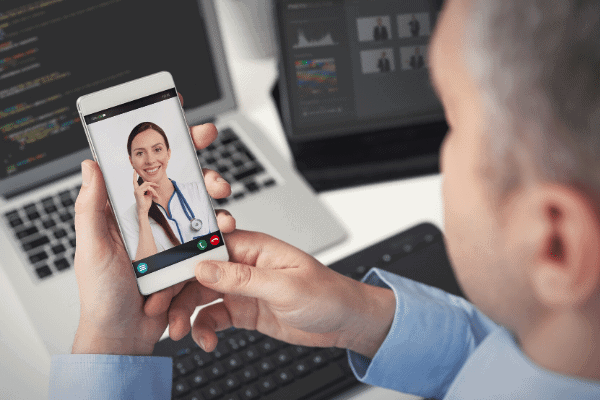
To reduce the spread of infection at the beginning of the pandemic, healthcare providers quickly adopted telehealth and remote patient monitoring (RPM) solutions to ensure continuity of care for various use cases, including chronic disease management, pregnancy, mental health and post-surgical recovery.
A few months later, major health systems teamed up to create a new standard for telehealth programs by moving previously hospitalized COVID-19 patients to home care settings, thus trailblazing the future of remote monitoring for pulmonary, cognitive, mobility and other health issues.
Today, with telehealth proven as a timely, safe and effective care delivery model, healthcare organizations are exploring long-term use to support patient care post-pandemic. Before going virtual, however, below are a few issues healthcare organizations should keep in mind.
Data Security and Trust
As an overwhelming number of patients shift to digital care delivery models that require them to share sensitive health information over home Wi-Fi networks, data security and trust will emerge as a key issue. Device manufacturers, government officials and health systems must enact contingency plans to address these vulnerabilities and understand that any problems that arise during the early stages of telehealth transformation will be pertinent to how healthcare consumers perceive digital health in the future.
Luckily, physical safety and digital security can be built into RPM systems to ensure that access to patient health information is provisioned on an as-needed basis and that electronic medical records and patient data meet HIPAA standards. In addition, where possible, patients and providers will look to alternatives to using patient Wi-Fi for transmissions, turning instead to carrier cellular connections. Cellular connected devices reduce patient technical requirements and can also improve usability and uptake.
Technical Challenges to the Consumer
Smart health devices such as the FitBit and other health monitoring equipment have gained mainstream appeal, which is an indication that more consumers recognize the pioneering benefits of RPM. By empowering users to manage their care remotely, doctors can improve patient engagement in the care process and drive greater satisfaction by resolving patient issues in real-time.
Even so, healthcare providers will need to ensure that the technology provided to patients is easy to use. When devices require significant setup and management tasks, the door opens to mistakes and frustration on the part of the patient and may require technical troubleshooting from the the provider and its partners.
Access to Reliable Connectivity
With RPM, healthcare professionals can attend to their patients quicker than ever before and expedite the initiation of essential treatments. However, RPM programs only work if patients have reliable internet connectivity because even just a little downtime can result in delayed diagnoses that negatively impact recovery times.
Therefore, ensuring access to reliable, secure internet connectivity is critical to closing gaps in care, especially in rural, low-income and medically underserved communities. Unfortunately, even in 2021, there are still millions of patients who do not have adequate at-home internet access and some who lack internet-connected devices. If we’re able to eradicate this access gap in a safe and reliable way (for example, through devices bespoke for telehealth), doctors will be able to connect remotely with patients in isolated areas and ensure every patient gets the care they need.
Interoperability
Remote patient monitoring requires telehealth solutions and hospitals to exchange information in a timely and HIPPA-compliant manner. Yet, securely relaying patient data from consumer devices to EHR (electronic health records) platforms and health care providers may not be possible for health systems working with outdated IT infrastructure.
This issue underscores the growing necessity for hospitals to overhaul obsolete IT systems in favor of more innovative digital health platforms. Thankfully, it appears a large portion of healthcare CIOs are recognizing the urgent need to digitally transform, with health IT spending slated to reach $140 billion by the end of 2021.
Conclusion
COVID-19 dramatically accelerated the innovation and adoption of remote patient monitoring and telehealth, revolutionizing the way physicians and health systems deliver care. However,
like most disruptive technologies that challenge the status quo, there are several hurdles standing in the way of RPM’s permanent uptake. Healthcare and tech leaders must collaborate to address the barriers listed above to ensure the benefits of RPM – such as stronger caregiver and patient relationships, improved patient outcomes, increased staff productivity and lower costs for healthcare providers – continue post-pandemic.
Dominic Marcellino is director of strategy and business development at Kajeet.
The Editorial Team at Healthcare Business Today is made up of skilled healthcare writers and experts, led by our managing editor, Daniel Casciato, who has over 25 years of experience in healthcare writing. Since 1998, we have produced compelling and informative content for numerous publications, establishing ourselves as a trusted resource for health and wellness information. We offer readers access to fresh health, medicine, science, and technology developments and the latest in patient news, emphasizing how these developments affect our lives.