Ensuring that eHealth software corresponds with all HIPAA security requirements paves the way for increased patient trust and higher quality treatment. Aren’t these the cornerstones of a better, more equitable approach to healthcare delivery?
By Vitaly Prus
In response to the global crisis provoked by the pandemic, companies the world over have had to adjust to serious, unforeseen circumstances and reassess their approach to delivering services. The healthcare industry is the one forced to grapple with the heaviest burden because, among other things, it must tackle the consequences of the outbreak.
To help overcome these challenging times, companies often accelerate the adoption of digital technologies, developing or incorporating eHealth software that’s more equipped to seamlessly provide appropriate treatment. This shift in methodology is impossible without storing massive amounts of sensitive patient data.
But how do we best safeguard all that data and oversee compliance to an access-based policy? The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is the foundation that we adhere to and build upon. Introduced almost 30 years ago, it helps confirm that names, addresses, medical records, financial data, and other electronic protected health information (ePHI) is secure.
Otherwise, data breaches affecting hundreds, thousands and, yes, even millions of individuals can (and do) occur. Apart from immense non-compliance penalties that can reach up to $1.8 million, patients’ trust is undermined, and as disclosing or safeguarding health details becomes more complicated, it degrades the quality of delivering healthcare.
The tip of the iceberg is enrollment into the Breach Notification Portal, most commonly known as the “Wall of Shame.” It contains the data on entities and violations where breaches adversely affected 500 or more patients. Once an organization gets on that list, it is increasingly difficult to rebuild their reputation and gain people’s trust.
Now that what’s at stake has been clearly defined, the remainder of this article focuses on QA tips and procedures that companies can undertake to ensure HIPAA software compliance.
Dealing with compliance testing: best practices to keep in mind
The development of HIPAA-compliant solutions is fraught with diverse challenges. Extensive amounts of data stored across various systems, the need to engage lawyers, medical officers, and other single-discipline experts, a large selection of available hospital platforms, and risk assessment avoidance — just to name a few.
So, it’s important to support such a sophisticated process with quality assurance. To eradicate possible cybersecurity failures and optimize QA processes, organizations can supplement their testing strategies by adhering to the following protocols:
- Start with a full-scale audit of technical infrastructure and ways that help protect a provider’s ecosystem from the actions of malicious intruders. During this step, the analysis of current software testing workflows also takes place to define errors that impede robust software delivery.
- As the majority of medical solutions possess a role-based approach to accessing ePHI, before testing it’s a good idea to compile a role grid to prioritize verifications based on the level of risk associated with each position.
- Rely on test automation to establish continuous compliance monitoring to confirm that updates or newly added components haven’t exposed any security vulnerabilities within the entire hospital, clinic or provider software ecosystem. Since this activity is both time- and effort-consuming, process automation will help accelerate it and minimize the human factor risks, which contributes to meeting quality benchmarks on time.
- After preparing in-depth reports for project stakeholders, the QA team should assist in incorporating suggested improvements, be it training sessions for employees to ensure high data safety or compiling a risk analysis practice to cope with a security gap should one emerge.
HIPAA compliance checklist to ensure high data protection
When it comes to people’s well-being and life expectancy, the stakes couldn’t be higher. The software must operate like clockwork, as any error can either affect health or cause inefficient treatment.
So, when confirming that the solution developed for hospitals meets set legal requirements, it’s worth performing penetration testing and vulnerability assessments. Fulfilled either manually or automatically, externally or internally, they’ll help uncover and define any security loopholes in the system and classify their severity levels. Doing so lowers the risk of data exposure in the future.
Depending on the application, its objective, and business need, the list of important aspects to pay attention to during testing may vary. However, most often the following areas of security standards deserve specific mention.
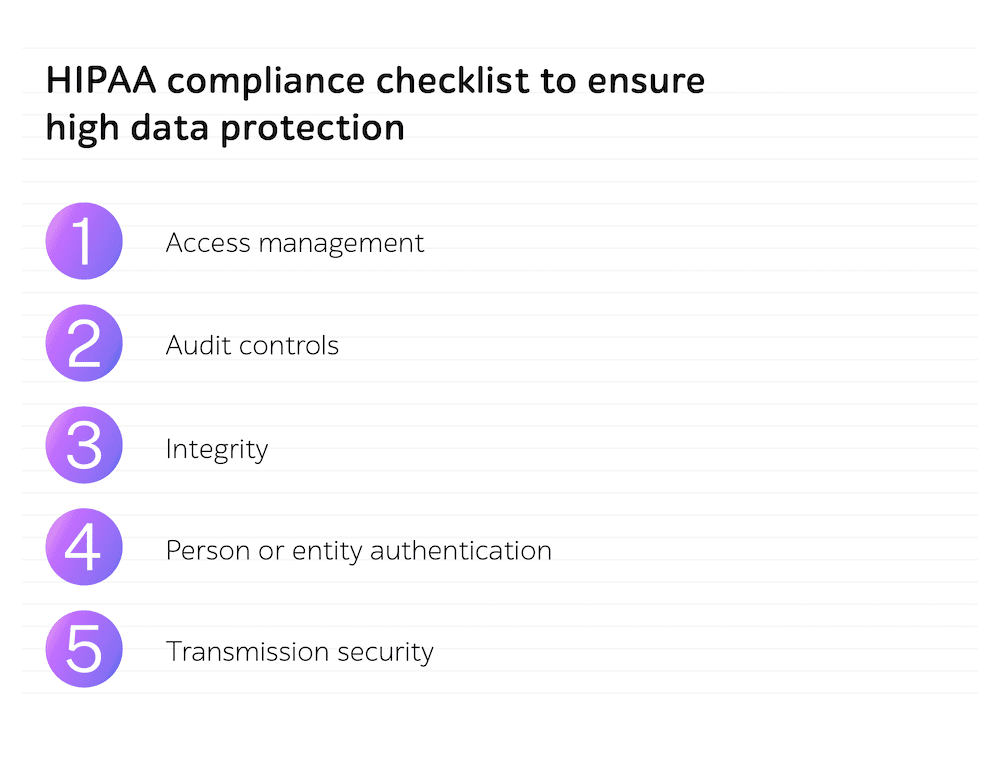
- Access management
One of the major demands for HIPAA compliance is accuracy ― a user must obtain the right to work with only the amount of information required to fulfill the activity. To make sure access provision is correct, the QA engineers check that unique usernames or numbers are applied to verify identity.
Especially vital is data availability during emergency situations that are determined by health provider entities, as patients’ lives may be on the line. So, it’s crucial to pay the utmost attention to testing.
Another major case to consider is checking that an automatic logoff feature activates without any delays after a set period of inactivity (e.g., if an employee forgets to log out, the system logs out automatically).
Finally, the QA engineers validate that ePHI is encrypted and decrypted sufficiently to decrease the probability of unauthorized access.
- Audit controls
To attain HIPAA compliance, it’s critical for covered entities to log activities that involve working with ePHI ― from altering to deleting anything in the health record. Make sure to verify that an in-depth description of data interactions made by all user types is recorded.
- Integrity
According to this standard, ePHI must be protected from inadequate modifications or deleting. If ePHI is destroyed either with or without human intervention, people’s data privacy could be compromised, and their lives may even be jeopardized. So, the QA team confirms that electronic security measures fully ensure data integrity and prevent any breaches by unauthorized users.
- Person or entity authentication
To ensure that the right person has entered the system and obtained privileged access to ePHI, covered entities can use a multi-stage authentication process. Called Privileged Access Management (PAM), it presupposes entering authenticating factors like credentials, keys, and biometrics. Whichever approach is chosen, the QA engineers verify that there are no malfunctions with the authentication process.
- Transmission security
Within an eHealth landscape, ePHI is regularly sent between diverse systems or front- and back-end parts. To ensure that it’s encrypted and delivered without any losses, changes, or unforeseen unauthorized access attempts, it’s vital to review the encryption algorithm being deployed, confirm the encryption of all data takes place, and compare sent and received information.
Summarizing
Safeguarding sensitive personal and health information is the key to avoiding a tarnished reputation. Stronger bonds are built with patients, as they are confident that provided data will never be revealed to outsiders. To enable such conditions, the QA teams need to emphasize HIPAA compliance testing, focusing on high software and information security.
Vitaly Prus is the Head of software testing department at a1qa.
With 15 years of experience in SQA, he has gained vast knowledge in both talent management and working with clients in a management role. One of his main activities as of now is implementing company policy and directing a strategy towards the profitable growth and operation of the company.
Now, QA department led by Vitaly consists of more than 190 engineers who have successfully completed over 200 projects across healthcare, retail, eCommerce, insurance, and other industries.
The Editorial Team at Healthcare Business Today is made up of skilled healthcare writers and experts, led by our managing editor, Daniel Casciato, who has over 25 years of experience in healthcare writing. Since 1998, we have produced compelling and informative content for numerous publications, establishing ourselves as a trusted resource for health and wellness information. We offer readers access to fresh health, medicine, science, and technology developments and the latest in patient news, emphasizing how these developments affect our lives.








