Robotics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are not newbies in the healthcare business. Robotics in healthcare have been around for many decades now. With the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, the rise of the aging senior population, and the healthcare system in crisis mode with a shortage of providers and resources, the use of AI and robotics in healthcare has garnered more attention and is becoming an integral part of the healthcare system.
While AI and robotics are frequently discussed in both the business and the hospital management world, I will discuss the increasing use of AI and robotics technology in healthcare from the stakeholder’s perspective.
Acceptance and adoption of the robotics system of care
AI and robotics are serving humanity in various forms and styles. For example, there are robot cleaners in hotels, robot waiters in restaurants, robot assistants in supermarkets, robots in warehouses to carry heavy loads of luggage, etc.. All of these have made us humans more accepting of the use of AI and robotics in our daily lives and have thus made the adoption of robotics for our healthcare more prevalent.
While acknowledging that there are many more ways AI and robotics have already penetrated into the healthcare system, here are three categories of AI and robotics that demonstrate the assistance being provided to healthcare stakeholders, and there is room for many more to come.
1) AI and Robotics assisting patients
(triage, rehabilitation/exoskeleton)
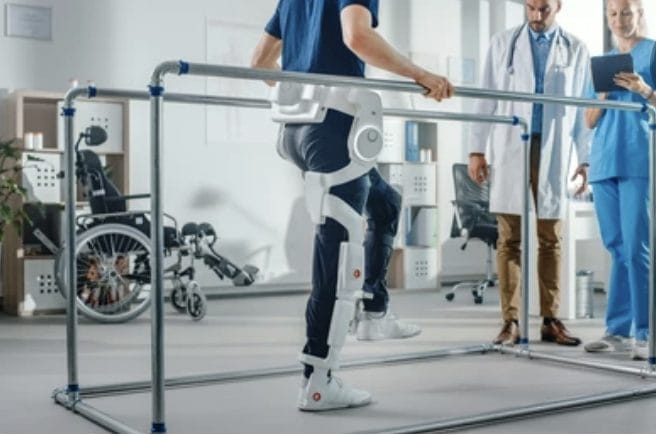

AI and Robotics have been assisting patients in various forms. There are AI algorithms and robotic systems that help triage patients and thus help them navigate to the needed provider in the process. For example, the Mayo Clinic uses AI algorithms that help triage a patient.(1) This became all the more useful during the pandemic, when the need became more apparent to implement social distancing.
There are various robotic technologies in the healthcare market that are geared toward aiding disabled individuals from war zones (e.g., the veteran population) or due to unfortunate diseases or injuries from accidents or crimes. These include robotic rehabilitation systems (exoskeletons), special assistant wheelchairs, and robot-assisted gait training that provide independence and strength to individuals with disabilities (2). Exoskeleton expert Mathew Marino says, “Whether people like it or not, they are a trendy, cool, sci-fi solution to problems people can all agree are worth solving. Who doesn’t want to see exoskeletons like Marvel’s Iron Man or Ripley’s Power Loader helping workers manage injuries, helping paralyzed patients walk, or protecting and augmenting soldiers?” (3).
2) AI and Robotics assisting providers
(surgeons)
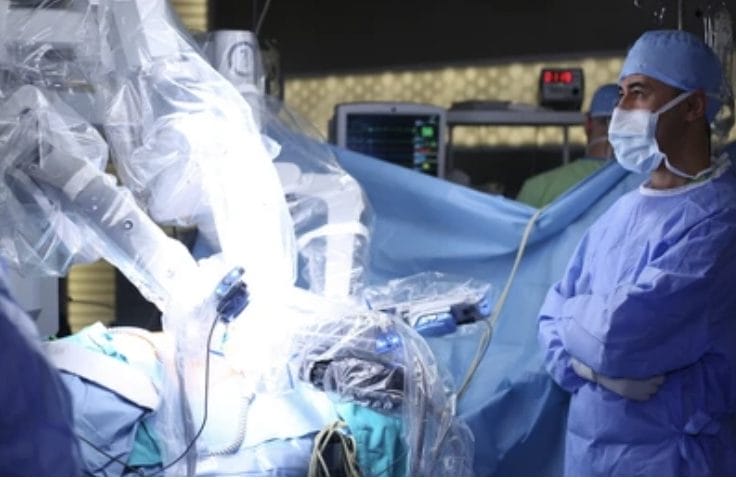
A robotic system that assists surgeons—the Da Vinci robotic system—has been in the market for more than two decades now. It started off being used in the field of urology (prostate-related surgeries) and is advancing fast; it has now penetrated into more specialties and fields like bariatrics and gynecology. Robotic surgeries have revolutionized the traditional way of performing surgeries, as it reduces patients’ pain and blood loss during surgeries, along with shorter post-op recovery periods. For surgeons, robotic-assisted surgeries give them more flexibility, precision, and control.
Tele-assistance using AI is another field that surgeons are using to train other surgeons remotely. Other robotics helping surgeons, include, but are not limited to, the MAKO system and ROSA system (4) for orthopedics and neurosurgeries, respectively.
3) AI and Robotics assisting hospital systems
(medical and non-medical tasks within the hospital workflows)
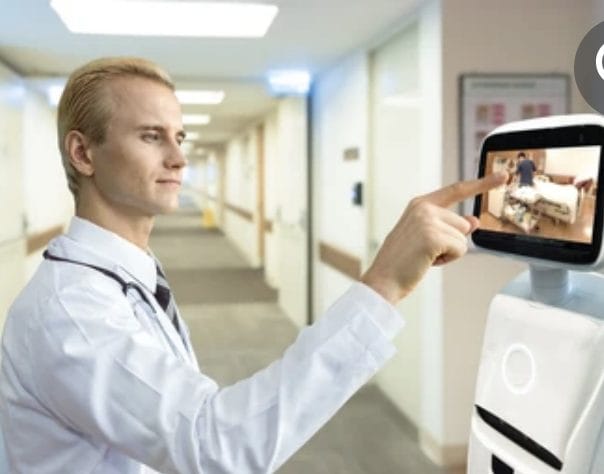

CareBot and ReceptionBot systems have shown to navigate the mobile robots within the hospital workflow, making tasks more convenient for the hospital management system.
AI and Robotic systems are also assisting hospital management teams with routine tasks, such as delivering medications to patients, collecting lab specimens, and managing patient appointments. One such example is the TUG robot system, which also helps clean and disinfect hospitals (5). These robots allow hospital staff members to pay attention to patients for more complicated tasks while performing repetitive tasks that do not require human intelligence.
Risks associated with AI and Robotics
Alongside these advantages, there are some unavoidable concerns and risks that accompany the use of robotics in healthcare. There is a rising concern of data breach not only in healthcare but almost in any industry, which could lead to the malfunction of the robot or an AI algorithm by an ill-intended person and thus could harm the patient. There is also the risk of compromising patient data privacy, as the company operating the robot would have access to patients’ private information.
There will always be a need of human supervision for all types of robots, especially in healthcare, because stakeholders could be in a vulnerable state during their use, and thus, we may not fully rely on robotics for our care.
While we are moving towards an era where robots will assist us in many aspects of our lives—from nurse robots to a robot waitress or a robot flight attendant—we cannot ignore the importance of human empathy and intelligence that may never be replaced with AI and robots.
References:
1) https://gbs.mayoclinic.org/licensable-content/symptom-triage.php
2) https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/exoskeleton-robotics
3) https://www.myontec.com/post/interviewing-wearables-and-exoskeleton-expert-matthew-marino
4) https://www.docwirenews.com/docwire-pick/robot-wars-in-medicine-mako-versus-rosa/
5) https://www.wired.com/2015/02/incredible-hospital-robot-saving-lives-also-hate/

Dr. Sahar Hashmi
About the Author:
Dr. Sahar Hashmi is the CEO of Myriad Consulting LLC - MA, USA. Hashmi is an MD with a PhD from MIT's Business School & IDSS with master in Systems Design and Management. She is a faculty instructor at Harvard and the Titan Business Award winner of 2022 for her creative consulting business.
Expertise: AI in healthcare, modern care delivery, digital health & business transformation and automation, data analytics, metaverse and smart homes/clinics/labs design.